The Problem
Iowa continues to have high rates of new cancers. Yet most people are unaware of the link between alcohol and cancer.
With these facts in mind, Iowa HHS created the ‘Straight Facts’ campaign. The purpose of the campaign is to educate Iowans on the link between alcohol use and cancer. When Iowans know more, they can make better choices for themselves.
The Facts
There is no one cause for cancer. Many factors play a role in developing cancer. Drinking alcohol raises your risk of developing several types of cancers. Drinking less alcohol helps lower the risk but does not remove the risk of cancer.
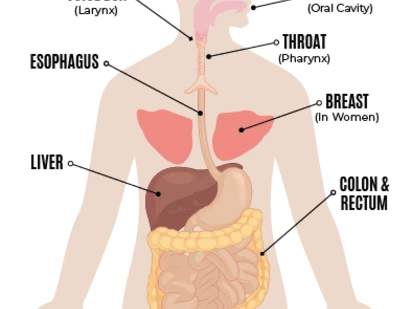
Alcohol is a known carcinogen. Studies show convincing evidence that alcohol is a risk factor for several cancers. These include mouth throat, voice box, and female breast cancers. Alcohol is also a risk factor for esophagus, liver, colon and rectum cancer.
Alcohol consumption is a leading cause of cancer which you can prevent. Alcohol ranks third after tobacco use and obesity.
- All types of alcoholic beverages, and any amount of drinking, increases one’s risk of cancer.
- The risk of cancer increases as the level of consumption increases. More drinks equal more cancer risk.
- Quitting alcohol use or cutting down long-term can lead to lower risk of some cancers.
- Less than half of adults know that alcohol may increase cancer risk.
Cancer in Iowa
Iowa continues to have the 2nd highest and fastest growing rate of new cancers in the U.S.
Iowa has the 4th highest incidence of alcohol-related cancers in the U.S., and the highest rate in the Midwest.
In 2019, the rate of alcohol-related cancers was almost 10% higher in Iowa than the U.S. average.
- Iowa currently ranks 2nd highest in the rate of new cases of mouth and throat cancer in the U.S.
- Iowa ranks 4th highest in the rate of new cases of esophageal cancer in the U.S.
- Iowa currently ranks 2nd highest in the rate of new cases of oral cavity and pharyngeal cancer in the U.S.
- Iowa ranks 8th highest in the rate of new cases of colorectal cancer in the U.S.
- Iowa ranks 9th highest in the rate of new cases of female breast cancer in the U.S.
- One risk factor that Iowans can change is alcohol use. This may be contributing to higher cancer rates.
Amounts Matter-The number of drinks matters
What is a "standard drink?"
In the U.S. a ‘standard drink’ equals any drink that contains about .06 fluid ounces or 14 grams of pure alcohol. Each of the drinks listed below contains approximately the same amount of alcohol.
- 12 fluid ounces of 'regular beer' with 5% alcohol content.
- 8-12 fluid ounces of malt liquor or flavored malt liquor, such as hard seltzer with 7% alcohol content.
- 5 fluid ounces of table wine with 12% alcohol content.
- 3-4 fluid ounces of fortified wine (such as sherry or port) with 17% alcohol content.
- 2-3 fluid ounces of cordial, liqueur or aperitif with 24% alcohol content.
- 1.5 fluid ounces of brandy or cognac with 40% alcohol content.
- 1.5 fluid ounces of distilled spirits (vodka, whiskey, etc.) with 40% alcohol content.
*The percentage of alcohol varies within and across beverage types. The standard drink guidelines shown may not be accurate for all alcohol retailers. Amounts may be different depending on the strength (% alcohol) of the drink in question. Visit Rethinking Drinking to help determine "standard drinks" per beverage.”
Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend one drink or less per day for women. Men should limit alcohol to two drinks or less per day.
Binge drinking consists of four or more drinks for women and five or more drinks for men in a two-hour period.
The more alcohol a person drinks, the higher the risk of cancer.
Any alcohol can increase one’s risk of cancer, but binge drinking poses the greatest risk.
Iowa ranks 4th highest in the nation for binge drinking in 2022. Binge drinking is drinking 5 or more drinks on one occasion for men and 4 or more drinks on one occasion for women. More than one fifth (22%) of Iowans report binge drinking, higher than the national average of 17%.
Binge drinking is also a concern among Iowa's youth. 15% of Iowans ages 12-22 reported binge drinking in 2019-2020.
What you can do to lower your cancer risk
Know the amount of alcohol you are drinking.
Any amount of alcohol reduction is likely to reduce one’s risk of cancer.
For those choosing to drink, drink in moderation. On days when drinking alcohol, limit intake to 2 drinks or less in a day for men and 1 drink or less in a day for women.
Some people should not drink at all. These include women who are pregnant or might be pregnant. People younger than 21 years of age should not drink. Some people should check with their doctor before drinking. These include people who have certain medical conditions. Some medications can interact with alcohol.
Tips for reducing drinking
Small changes can make a big difference. It’s up to you to decide whether to change your drinking. Here are some tips that can help:
- Make a plan.
- Keep track of each drink you consume.
- Know if you are drinking a ‘standard drink’ or something more.
- Determine your motivations and goals for drinking less.
- Set goals for the number of days you will drink and/or the number of drinks you will have and stick to them.
- Practice saying “no thanks” to an alcohol drink if someone offers one.
- Consider non-alcoholic substitutes, such as non-alcoholic beer or “mocktails”.
- Find alternatives to drinking – start a new hobby or renew an old one.
- Avoid situations and trigger that cause you to drink.
- Tell family and friends of your plan and ask for their support.
- Keep trying – don’t let setbacks deter you.
- Use resources to help, such as Check Your Drinking. Make a Plan to Drink Less.
- Ask for professional help from a doctor or treatment agency if needed.
Citations
- Cancer in Iowa – 2024 Alcohol-Related Cancers. Iowa Cancer Registry. cancer-in-iowa-2024.pdf
- Alcohol and Cancer Risk. The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory 2025. Alcohol and Cancer Risk | HHS.gov
- Alcohol Use and Your Health. Alcohol Use and Your Health | Alcohol Use | CDC
- Alcohol’s Effects on Health. Alcohol's Effects on Health | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
- Alcohol and Cancer Risk. Alcohol and Cancer Risk Fact Sheet - NCI
- Guidance on Alcoholic Beverages in the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. Guidance on Alcoholic Beverages in the Dietary Guidelines for Americans | Dietary Guidelines for Americans
- 12 Ways to curb your drinking. 12 ways to curb your drinking - Harvard Health